Audiometric configurations at a given frequency are classified into 12 patterns, and these patterns are grouped into four series.
In a pattern [4-0], typical plateaus for both AC and BC in the left, poorer ear by AC are obtained. In the right ear , plateaus are not present.
The AC threshold measured without masking in the left ear (AL0) is the shadow hearing threshold, and the true AC threshold in the left ear (AL*) is AL0 plus ω (ω = AL*– AL0)). Then, the AC and BC plateau widths of the left ear (Lt APW, Lt BPW) are described below:

Here, the difference between the AC thresholds measured without masking at some frequency is termed air and air gap (AA gap), and the Lt and Rt represent left and right, respectively:
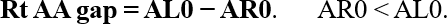
The difference between the true BC thresholds (BL* and BR*) is termed a relative amount of sensorineural component of the left ear compared to the right ear (Lt SNC):
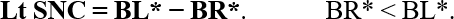
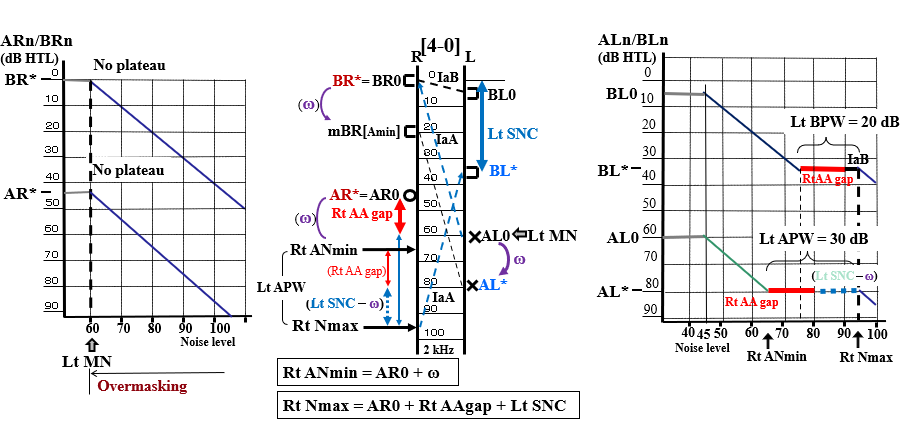
AA gaps serve as a clear indicator to predict the difficulty level of masking.
<Abbreviation>
- AR0, BR0: the AC, BC threshold without masking in the right ear
- AR*, BR* the true AC, BC threshold in the right ear
- AL0, BL0: the AC, BC threshold without masking in the left ear
- AL*, BL* the true AC, BC threshold in the left ear
- IaA: the interaural attenuation for AC signals
- IaB: the interaural attenuation for BC signals
- ANmin: the minimum adequate masking noise level for AC
- Nmax: the maximum adequate masking noise level
Click the following website for more information.
Masking theory in pure tone audiometry – systematic lectures –
(https://izumo-yaegaki.jp).
 PDF file
PDF file